The direct method of the
sphere segmenting at 3d-modeling of the Earth surface
Author: Grishin Maxim Leonidovich
Contact information:
Keywords: GIS, direct sphere segmenting, icosahedron, 3d-modeling, transformation of the
coordinates.
Thesis form: 4th International Conference Earth From Space:
The Most effective Solutions. Abstracts. 2009. – P.
109-110. – ISBN 978-5-9518-0378-8.
Title of the session: Technologies and software for data
processing – 3-D modeling.
The development of 3d-GIS of the planet
scale demands a fresh qualitative approach to the question of segmenting of
cartographic information. The methods of segmenting developed for planar
cartography are not satisfactory, moreover in some
cases they are irrelevant. For that matter the method of direct method of
sphere segmenting is introduced (pic. 1), it
possesses much better quality of segmenting mesh to compare with widely used
segmenting by geodetic lines.
For providing the direct (with the
possibility to calculate
the node coordinates of the any deepness fragmentation at once)
segmenting, the special system of coordinates is worked out, it consists of 10
meshes, which are based on the icosahedron, and the
each of them consists of two spherical triangles. The coordinates of semi-mesh
(pic. 2) are formed by the method of subdivision of the surface with two
sheaf of planes, which directing lines are calculated with the formula:
![]() , (1)
, (1)
![]() . (2)
. (2)
The transition to the special coordinate system
for the point ![]() is achieved with two stages: the defining of
the basic semi-segment and calculating the local coordinates
is achieved with two stages: the defining of
the basic semi-segment and calculating the local coordinates ![]() that is equal to
that is equal to ![]() and
and ![]() that is equal to
that is equal to ![]() , with the
following normalization for
, with the
following normalization for ![]() .
.
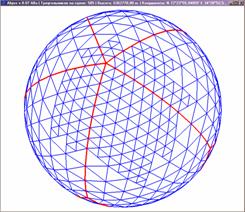
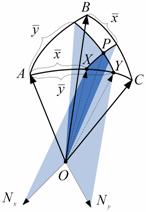
Pic.
1
Pic.2
The reverse transformation of the local
coordinates can be observed as the definition of the cross point of three planes:
![]() . (3)
. (3)
As far all the edges of icosahedron are equal, and the
segmentation is completed by subdivision of the angle at the adjoining apexes,
the nodes at the borderline of the adjoining coordinate meshes sharply coincide.
It provides the seamless joining between the base segments.
During the work process the
segmenting quality rating was achieved, they inform about the possibility of tiling
realization of the landscape on the whole surface of a planet. Combining with
the technology of the quad-tree the method provides the effective rendering and
a fast access to the data with geographic binding. As far as transformation of
the coordinates of the method is reversible there are no any difficulties with
interlinked exchange of cartographic information between the existing GIS’s and
those that will use the introduced method.